ODN 2395 control
| Product | Unit size | Cat. code | Docs. | Qty. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ODN 2395 control Negative control for ODN 2395 |
Show product |
1 mg |
tlrl-2395c-1
|
|
Negative control for ODN 2395 - Class C CpG oligonucleotide - Human/Mouse TLR9-preferred ligand
No TLR9 activation with ODN 2395 Control
 InvivoGen also offers:
InvivoGen also offers:
• TLR reporter cells: HEK293, RAW, THP-1 cells
• TLR research tools: Antibodies, Inhibitors, etc.
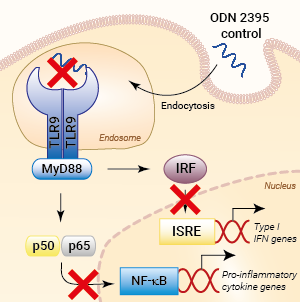
ODN 2395 Control is designed as a negative control for the TLR9 agonist ODN 2395. ODN 2395 is an immunostimulatory Class C CpG oligonucleotide (ODN), specific for the human and murine Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) [1]. It is a short synthetic single-stranded DNA molecule containing unmethylated CpG dinucleotides (CpG motifs). These unmethylated CpG motifs mimic microbial DNA and act as immunostimulants via TLR9.
Mode of action
Stimulatory CpG ODNs are internalized and activate the endosomal receptor TLR9. Activation of TLR9 triggers NF-κB- and interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-mediated pro-inflammatory responses upon the recognition of unmethylated cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanosine (CpG) forms of DNA [2-4]. Unmethylated CpG dinucleotides are a hallmark of microbial (bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasite) DNA and mitochondrial self-DNA [4, 5]. Class C CpG ODNs, such as ODN 2395, combine classes A and B features. They contain a complete phosphorothioate (PS) backbone and a CpG-containing palindromic motif. They strongly induce B cell stimulation as well as IFN-α production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells [6].
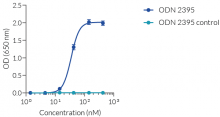
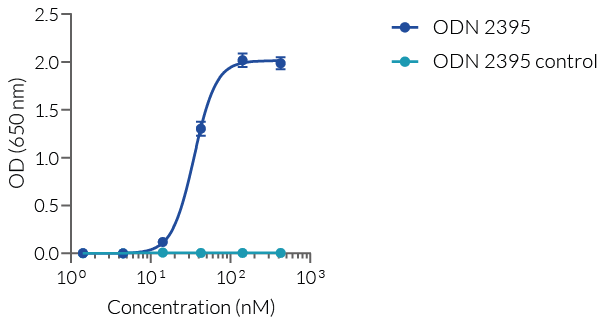
InvivoGen's ODN 2395 contains GpC dinucleotides instead of CpGs and does not induce TLR9 activity. In HEK-Blue™ mTLR9 and hTLR9 reporter cells, ODN 2395 Control does not activate TLR9 compared to the immunostimulatory ODN 2395 (see figure and data not shown).
Key features of ODN 2395 Control
- Negative control of human and mouse TLR9-activating ODN 2395
- Synthetic ODN with unmethylated GpC motifs
- Each lot is functionally tested
- High-quality, pre-clinical ODN 2395 VacciGrade™ is also available for in vivo studies
![]() Get more information about CpG ODNs Classes.
Get more information about CpG ODNs Classes.
![]() Read our review on TLR9 agonists: double-edged sword for immune therapies.
Read our review on TLR9 agonists: double-edged sword for immune therapies.
References
1. Roda JM. et al., 2005. CpG-containing oligodeoxynucleotides act through TLR9 to enhance the NK cell cytokine response to antibodycoated tumor cells. J Immunol. 175(3):1619-27.
2. Kumagai Y. et al., 2008. TLR9 as a key receptor of the recognition of DNA. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 60(7):795-804.
3. Heinz L.X. et al., 2021. TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7-9. Nature. 581(7808):316-322.
4. Kayraklioglu N. et al., 2021. CpG oligonucleotides as vaccine adjuvants. DNA Vaccines: Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 2197. p51-77.
5. Kumar V., 2021. The trinity of cGAS, TLR9, and ALRs: guardians of the cellular galaxy against host-derived self-DNA. Front. Immunol. 11:624597.
6. Jurk M. et al., 2004. C-Class CpG ODN: sequence requirements and characterization of immunostimulatory activities on mRNA level. Immunobiology. 209(1-2):141-54.
Specifications
Specificity: Negative control of the human/mouse TLR9-preferred ODN 2395
Working concentration: 1-5 µM
Solubility: 5 mg/ml in water
ODN 2395 Control sequence
5’-tgctgcttttggggggcccccc -3’ (22 mer)
Note: Bases are phosphorothioate.
Quality control:
- The absence of mouse and human TLR9 activation has been tested using HEK-Blue™ TLR9 cells.
- The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK-Blue™ TLR4 cells.
Contents
- 1 mg (141.85 nmol) lyophilized ODN 2395 Control
- 1.5 ml sterile endotoxin-free water
![]() ODN 2395 Control is shipped at room temperature
ODN 2395 Control is shipped at room temperature
![]() Upon receipt, store -20°C.
Upon receipt, store -20°C.
Details
CpG ODNs
Synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides containing unmethylated CpG motifs (CpG ODNs), such as ODN 1018, have been extensively studied as adjuvants [1]. These CpG motifs are present at a 20-fold greater frequency in bacterial DNA compared to mammalian DNA [2]. CpG ODNs are recognized by the Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9), which is expressed on human B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), thereby inducing Th1-dominated immune responses [3]. Pre-clinical studies, conducted in rodents and non-human primates, as well as human clinical trials, have demonstrated that CpG ODNs can significantly improve vaccine-specific antibody responses [1]. Three types of stimulatory CpG ODNs have been identified, types A, B, and C, which differ in their immune-stimulatory activities [4-5].
Toll-like receptor 9
The Toll-like Receptor 9 (TLR9) is an endosomal receptor that triggers NF-κB- and interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-mediated pro-inflammatory responses upon the recognition of unmethylated cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanosine (CpG) forms of DNA [6-8]. Unmethylated CpG dinucleotides are a hallmark of microbial (bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasite) DNA, as well as mitochondrial self-DNA [8,9]. These TLR9 agonists can be mimicked by synthetic oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs (CpG ODNs), which have been extensively studied to improve adaptive immune responses in the context of vaccination [6,8].
TLR9 is mainly expressed in subsets of Dendritic Cells and B cells of all mammals. In rodents, but not in humans, TLR9 is also expressed in monocytes and macrophages [8]. The structure of the receptor varies by 24% between human TLR9 (hTLR9) and mouse TLR9 (mTLR9) [8]. They recognize different CpG motifs, the optimal sequences being GTCGTT and GACGTT for hTLR9 and mTLR9, respectively [10].
References:
1. Steinhagen F. et al., 2011. TLR-based immune adjuvants. Vaccine 29(17):3341-55.
2. Hemmi H. et al., 2000. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature 408:740-5.
3. Coffman RL. et al., 2010. Vaccine adjuvants: Putting innate immunity to work. Immunity 33(4):492-503.
4. Krug A. et al., 2001. Identification of CpG oligonucleotide sequences with high induction of IFN-alpha/beta in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol, 31(7): 2154-63.
5. Marshall JD. et al., 2005. Superior activity of the type C class of ISS in vitro and in vivo across multiple species. DNA Cell Biol. 24(2):63-72.
6. Kumagai Y. et al., 2008. TLR9 as a key receptor of the recognition of DNA. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 60(7):795-804.
7. Heinz L.X. et al., 2021. TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7-9. Nature. 581(7808):316-322.
8. Kayraklioglu N. et al., 2021. CpG oligonucleotides as vaccine adjuvants. DNA Vaccines: Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 2197. p51-77.
9. Kumar V., 2021. The trinity of cGAS, TLR9, and ALRs: guardians of the cellular galaxy against host-derived self-DNA. Front. Immunol. 11:624597.
10. Bauer S. et al., 2001. Human TLR9 confers responsiveness to bacterial DNA via species-specific CpG motif recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98(16):9237-42.